In the dynamic realm of digital advertising, the choice between native ads and display ads is pivotal for marketers seeking maximum impact. Each offers distinct advantages, catering to diverse marketing objectives and audience preferences. Native ads seamlessly blend into content, while display ads command attention with visual flair. This guide delves into the nuances of these two advertising powerhouses, providing valuable insights to help you make an informed decision. By understanding the strengths and applications of native and display ads, you can tailor your advertising strategy to reach your target audience effectively and achieve your campaign objectives. Let’s explore the battle of native ads vs. display ads.
Table of context
Importance of Understanding the Differences
Definition of Native Ads
Native ads seamlessly blend into their surrounding content, mirroring the form and function of the platform they appear on. They aim to provide a non-disruptive user experience while promoting a product or service.
Definition of Display Ads
Display ads are visually prominent and designed to grab attention through banners, images, and multimedia elements. They’re typically placed in designated ad spaces on websites, distinct from the site’s organic content.
Importance of Understanding the Differences
Distinguishing between native and display ads is crucial for marketers. It guides content creation and placement strategies, ensuring campaigns resonate with audiences effectively. This understanding optimizes user engagement, click-through rates, and overall campaign success.
Native Ads Explained
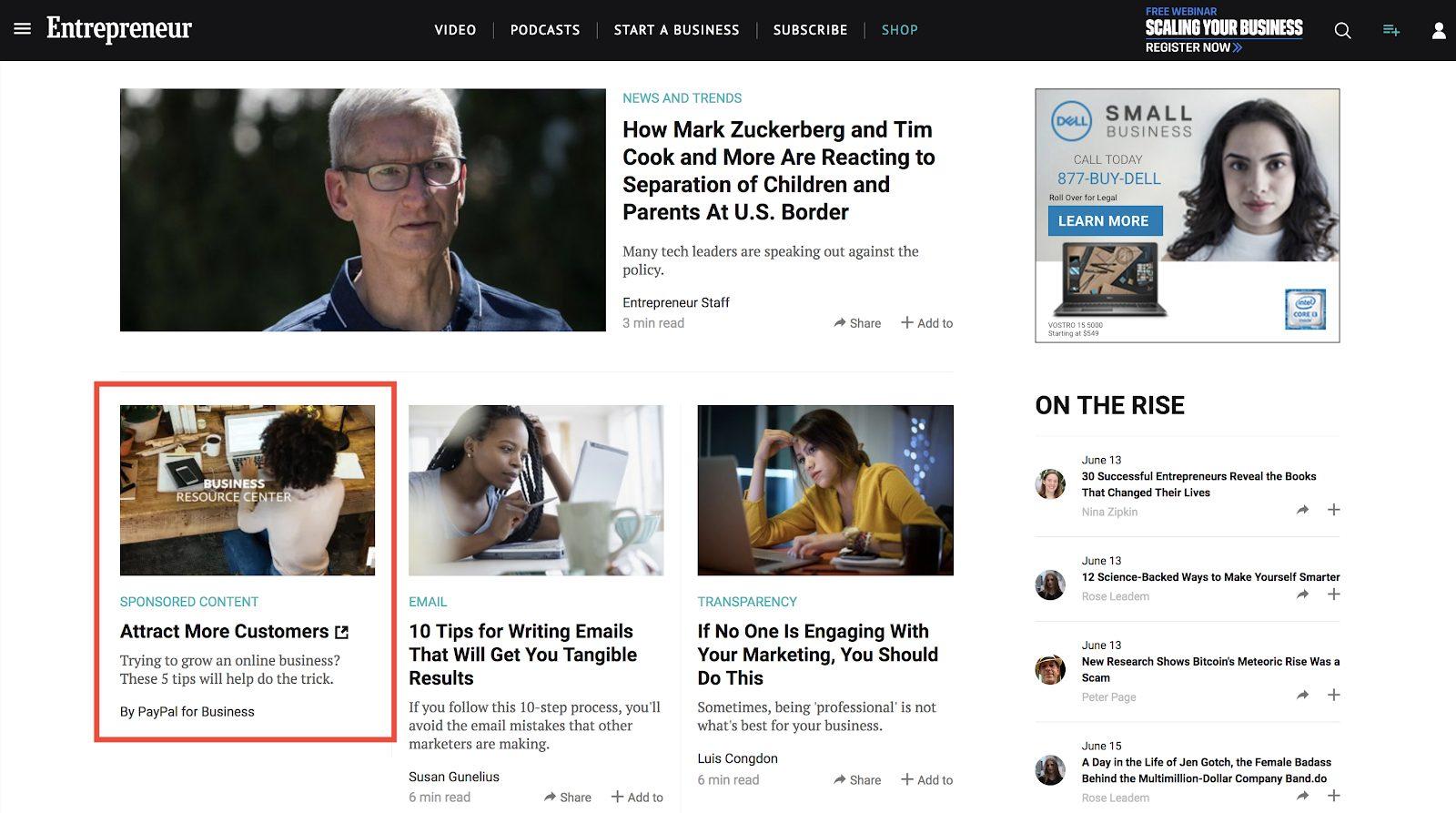
When we discuss native ads vs. display ads, obtaining an in-depth knowledge of both is essential. Native advertising has revolutionized the digital marketing landscape with its ability to seamlessly integrate promotional content into the user’s browsing experience. Understanding the distinctive characteristics and types of native ads provides marketers with a powerful tool for engaging their target audience effectively.
Characteristics of Native Ads
Integration with Content:
Native ads are designed to blend harmoniously with the surrounding content, adopting the look and feel of the platform they appear on. This integration ensures that the promotional material feels organic and non-intrusive, enhancing the user experience.
Non-Disruptive Format:
Unlike traditional interruptive advertising methods, native ads do not disrupt the user’s browsing flow. Instead, they provide relevant and valuable information, creating a more seamless transition between the ad and the content.
Match with Platform’s Style:
Native ads are meticulously crafted to align with the style, tone, and design of the platform. This adaptability ensures that the ad appears as a natural extension of the content, resonating with the audience in a way that traditional ads often struggle to achieve.
Types of Native Ads
In-Feed Ads:
These creative ads appear within the content feed of a platform, such as social media feeds or news websites. They maintain a similar format to the surrounding content, allowing them to flow seamlessly within the user’s browsing experience.
Sponsored Content:
Sponsored content involves creating articles, videos, or other forms of content that are funded by an advertiser. This content is then published on a platform, often marked as “sponsored,” and provides value to the audience while subtly promoting a product or service.
Recommendation Widgets:
These widgets suggest related articles, products, or services based on the user’s browsing behavior. They appear at the end of articles or within designated sections, subtly encouraging further exploration.
Benefits of Native Ads
Improved User Engagement:
Native ads captivate audiences by providing relevant and valuable information, leading to higher levels of engagement. By seamlessly integrating with content, they naturally draw the user’s attention.
Higher Click-Through Rates (CTRs):
Due to their non-disruptive nature and relevance, native ads often achieve higher click-through rates compared to traditional display ads. Users are more inclined to interact with content that feels integrated and valuable.
Enhanced User Experience:
Native ads contribute to a positive browsing experience by offering content that aligns with the user’s interests. This leads to increased trust and a more favorable perception of the brand or product being promoted.
Display Ads Explained
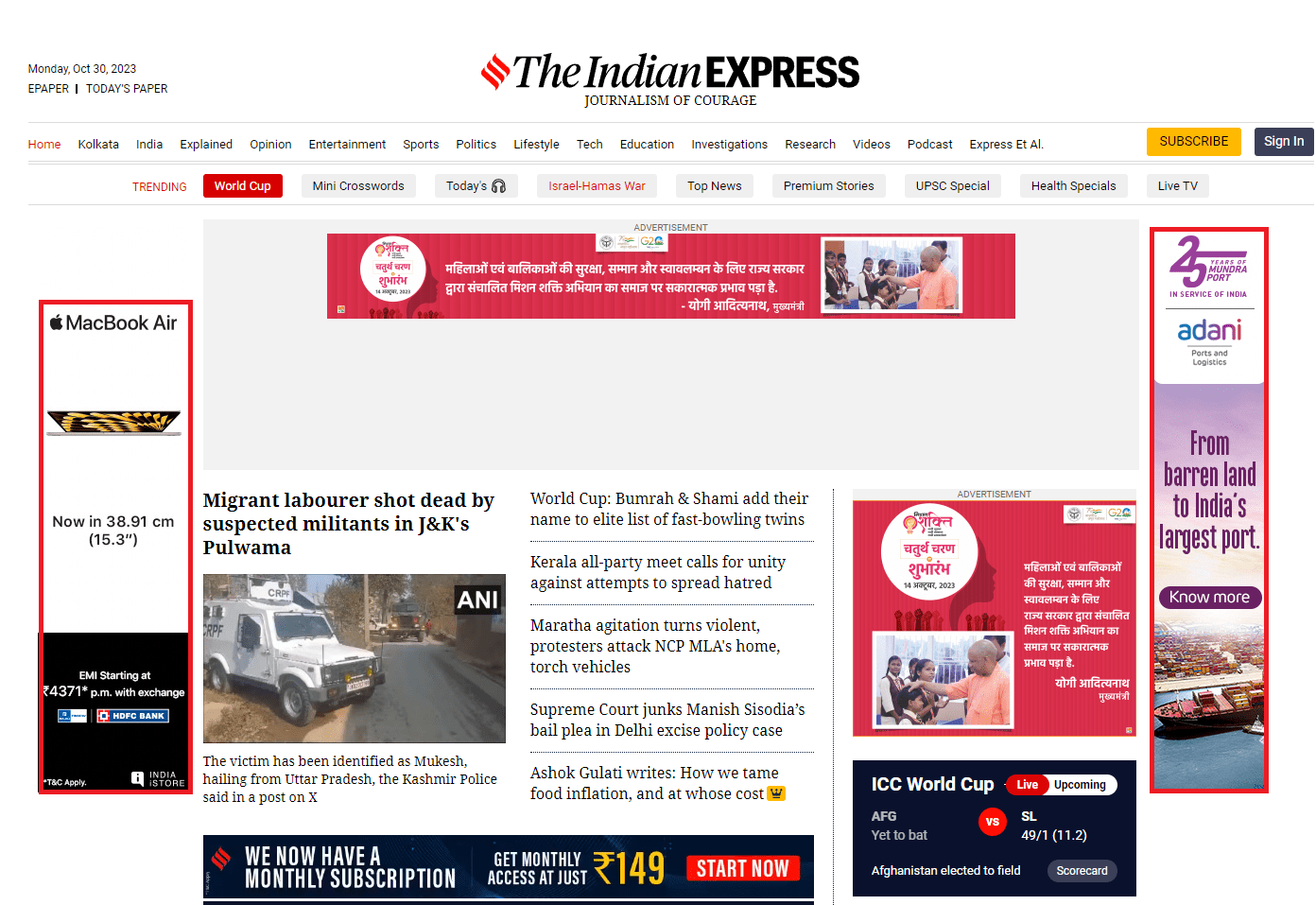
To determine the best in the battle of native ads vs. display ads, it is essential to know about both. Display advertising, a cornerstone of digital marketing, leverages visual elements to capture the attention of potential customers. Understanding its characteristics, types, and benefits empowers marketers to utilize display ads effectively in their campaigns.
Characteristics of Display Ads
Visual Banner or Text:
Display ads predominantly rely on visual elements, including images, graphics, and text, to convey the promotional message. They are designed to be eye-catching and visually appealing.
Placement on Websites:
Display ads are strategically positioned on websites, often in designated ad spaces. They can appear on various pages, such as homepages, article pages, or product pages, maximizing their visibility.
Standard Ad Formats (e.g., Banners, Skyscrapers):
Display ads adhere to standardized formats, including banners (horizontal rectangles) and skyscrapers (tall vertical rectangles). These formats ensure consistency across different platforms and websites.
Types of Display Ads
Banner Ads:
Banner ads are one of the most common forms of display advertising. They appear at the top, bottom, or sides of a webpage, aiming to grab the user’s attention with visually appealing graphics and concise messaging.
Video Ads:
Video ads leverage dynamic audio-visual content to convey the message. They can be auto played or initiated by the user, providing an engaging medium for storytelling and product demonstrations.
Pop-Up Ads:
Pop-up ads appear in a separate window or overlay on top of the main content, demanding the user’s immediate attention. While they can be effective, they should be used judiciously to avoid disrupting the user’s experience.
Benefits of Display Ads
Broad Reach and Visibility:
Display ads have the potential to reach a wide audience across various websites and platforms. This broad exposure increases the likelihood of capturing the attention of potential customers.
Targeting Capabilities:
Advanced targeting options allow marketers to tailor display ads to specific demographics, interests, and behaviors. This precision ensures that the ad is shown to the most relevant audience, maximizing its effectiveness.
Brand Awareness:
Display ads play a crucial role in building brand recognition and awareness. The visual impact of these ads reinforces the brand’s identity, making it more memorable for potential customers.
Key Differences Between Native and Display Ads
Now that we know everything about native ads vs. display ads, let’s discover the key differences between them. Native and display ads represent two distinct approaches to digital advertising, each with its own set of characteristics and benefits. Understanding the key differences between them is essential for marketers to make informed decisions about which format aligns best with their campaign objectives and target audience.
| Elements | Native Ads | Display Ads |
|---|---|---|
| Format and Appearance |
|
|
| Integration with Content |
|
|
| User Experience |
|
|
| Engagement Levels |
|
|
| Click-Through Rates (CTRs) |
|
|
| Platform Suitability |
|
|
When to Use Native Ads?
Native ads are a versatile and effective tool in the digital marketing toolkit. Knowing when to employ them can greatly enhance their impact on the target audience.
Content-Driven Campaigns:
Native ads are invaluable in content-driven campaigns. They seamlessly blend with the surrounding content, providing value to the user while subtly promoting a product or service. This approach fosters a positive user experience, making it ideal for content-centric marketing efforts.
Social Media Platforms:
Social media platforms are fertile ground for native advertising. Users engage with content in a highly interactive manner, and native ads can organically become part of their feed. This facilitates higher user engagement and interaction with the ad content.
Mobile Optimization:
With the surge in mobile device usage, native ads are essential for mobile optimization. They adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and orientations, ensuring a consistent and non-intrusive experience for mobile users.
Niche Markets:
Native ads are particularly effective in niche markets or industries with specialized audiences. By integrating seamlessly with industry-specific content, they resonate more profoundly with the target demographic, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
When to Use Display Ads
Google display ads are a powerful tool for capturing attention and raising brand awareness. Employing them strategically can yield significant results in various marketing scenarios.
Brand Awareness Campaigns:
Display ads excel in brand awareness campaigns. Their visually striking nature ensures that the brand’s message is prominently displayed, making a lasting impression on the audience.
Remarketing Strategies:
Display ads are instrumental in remarketing efforts. They re-engage users who have previously interacted with a website or shown interest in a product or service. Display ads serve as timely reminders, encouraging users to revisit and convert.
Targeting Broad Audiences:
When the objective is to reach a wide audience, display ads are the go-to choice. Their visually appealing format ensures they grab attention, making them effective for casting a wide net and generating interest.
Visual Impact Emphasis:
In campaigns where visual impact is paramount, display ads shine. They utilize captivating images, graphics, and multimedia elements to convey the message. This is particularly effective for products or services where visuals play a significant role in consumer decision-making.
Cost Models for Native Ads
Cost Per Click (CPC):
In the cost-per-click or CPC model, advertisers pay a fee each time a user clicks on their native ad. This model is performance-based, ensuring that advertisers only pay for actual clicks, making it a cost-effective option for driving traffic to a website or landing page.
Cost Per Mille (CPM):
CPM is a pricing model where advertisers pay a set fee for every thousand impressions (views) of their native ad. While it doesn’t guarantee clicks, it can be effective for brand exposure and awareness campaigns, as advertisers pay for ad views rather than interactions.
Cost Per View (CPV):
CPV involves advertisers paying a fee each time a user views a video ad. This model is commonly used in video native advertising, allowing marketers to gauge the cost-effectiveness of their video content based on views.
Cost Models for Display Ads
CPM vs. CPC:
Display ads offer a choice between CPM and CPC models. CPM charges advertisers per thousand impressions, regardless of clicks, while CPC charges per click. Advertisers choose based on their campaign goals, with CPM focusing on brand exposure and CPC on driving traffic.
Cost Per Viewable Thousand Impressions (vCPM):
vCPM is a model that charges advertisers for viewable impressions only, ensuring that they pay for ad views that are actually seen by users. This model improves ad effectiveness and provides greater transparency in terms of ad visibility.
Cost Per Engagement (CPE):
CPE is a model tailored for interactive display ads. Advertisers pay when users engage with the ad, which could include actions like clicks, form submissions, or video interactions. This model is ideal for campaigns that prioritize user interaction and engagement metrics.
Effectiveness Metrics
The effectiveness of both native and display ads can be assessed through a combination of engagement metrics, CTR, and conversion tracking. These metrics offer valuable insights into user behavior and the impact of advertising efforts, allowing marketers to refine their strategies for optimal results.
Measuring Native Ad Success
Engagement Metrics (Likes, Comments, Shares):
Engagement metrics gauge how effectively native ads resonate with the audience. Likes, comments, and shares indicate active interest and interaction. High engagement levels signify that the content is relevant and engaging, indicating a successful native ad campaign.
Click-Through Rate (CTR):
CTR measures the effectiveness of native ads in driving user traffic to a designated landing page. It is calculated by dividing the number of clicks by the number of impressions. A higher CTR indicates that the ad successfully compelled users to take action, demonstrating its impact.
Conversion Rate:
The conversion rate assesses the percentage of users who completed a desired action after interacting with a native ad. This action could range from making a purchase to signing up for a newsletter. A high conversion rate signifies that the native ad effectively persuaded users to take the intended action, demonstrating its effectiveness in achieving campaign goals.
Measuring Display Ad Success
Impressions and Reach:
Impressions measure the total number of times a display ad is viewed by users. Combined with reach, which quantifies the number of unique users who viewed the ad, these metrics provide insight into the extent of brand exposure. Higher impressions and reach values indicate broader audience engagement.
Click-Through Rate (CTR):
CTR for display ads mirrors its counterpart in native advertising. It calculates the ratio of clicks to impressions and reflects how effectively the ad encourages user interaction. A higher CTR indicates that the display ad successfully prompted users to take action, showcasing its effectiveness.
Conversion Tracking:
Conversion tracking is paramount for measuring the success of display ads. It evaluates the number of users who completed a specific action after interacting with the ad, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service. A high conversion rate indicates that the display ad was influential in driving user actions, indicating its effectiveness in achieving campaign objectives.
Conclusion
In the battle of native ads vs. display ads, determining anyone of them as the best is difficult since both have their respective impact of marketing. Native ads seamlessly integrate with content, providing a non-disruptive user experience, while display ads command attention with visual elements. Understanding these distinctions empowers marketers to utilize each format effectively. Selecting between native and display ads hinges on campaign objectives and target audience preferences. Native ads excel in content-driven, niche markets, while display ads shine in brand awareness initiatives and broad audience targeting.
Hire a professional digital marketing company in Kolkata to leverage the power of ad marketing.
More reasons to trust us!
Excellis IT is building a skilled team in IT support, customer support, digital marketing, and back-office services for modern companies.

Excellis it is an esteemed ISO/IEC 27001:2022 certified company

We achieved the prestigious certification by MSME in 2019

We are certified by the Central Vigilance Commission

We are an honoured members of NASSCOM since 2022






